Last Updated on January 8, 2026 by Triumphoid Team
The digital marketing landscape is shifting faster than ever. What was once considered “advanced automation” is now baseline, driven by machine learning and the impending cookieless future.
Whether you are a sole entrepreneur building your first automated sequence or a Chief Marketing Officer optimizing a complex MarTech stack, fluency in these terms is the essential foundation for converting prospective customers and scaling revenue.

To give you a powerful boost of Marketing Automation and Technology (MarTech) fluency, we’ve updated and expanded this glossary of over 70 terms every modern marketer must know.
📚 Marketing Automation & MarTech Glossary
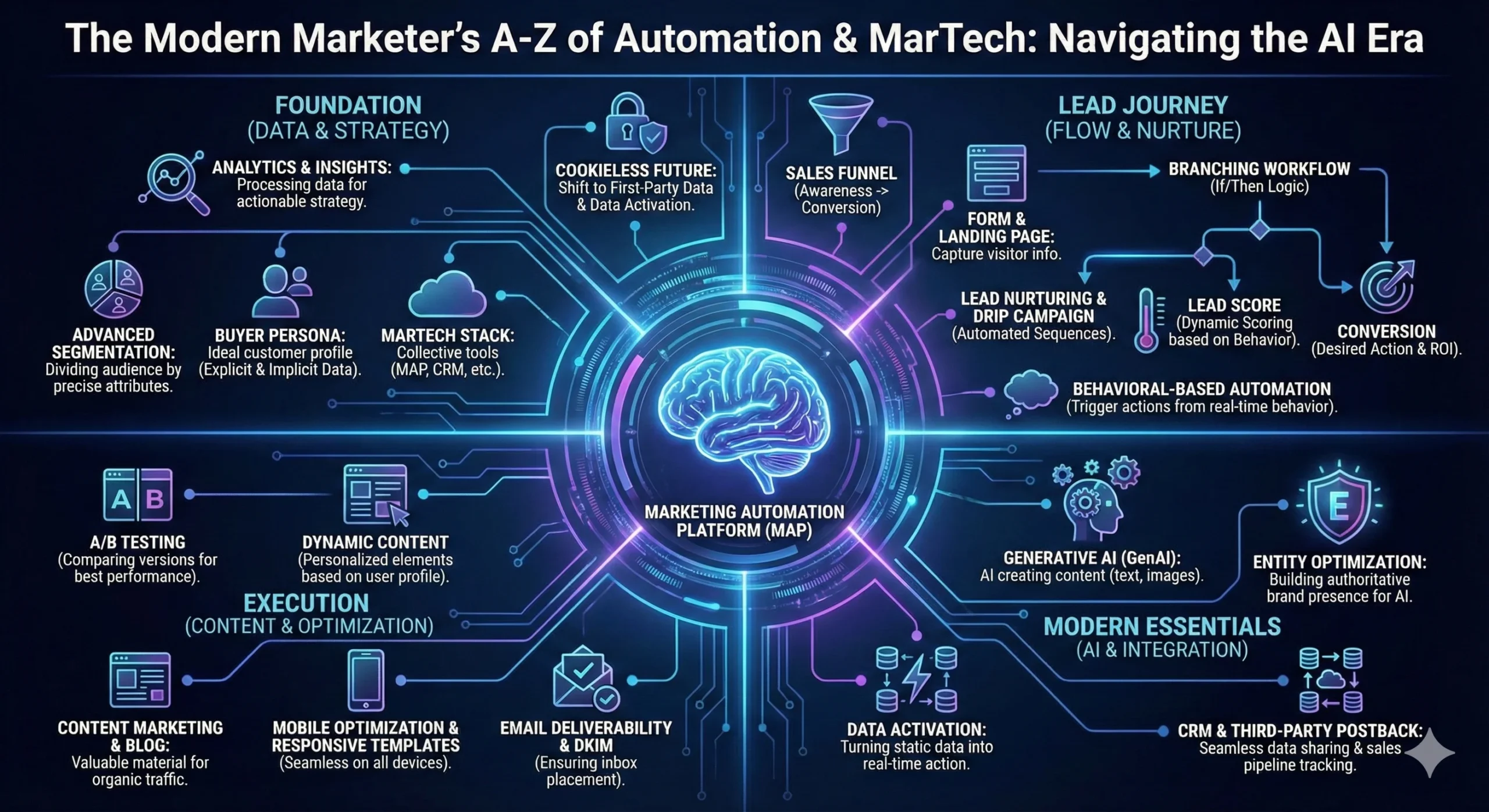
A
A/B Testing
The systematic comparison of two versions (A and B) of a marketing asset (email, landing page, CTA) to determine which performs better against a specific goal, typically improving the Conversion Rate. Also known as: Split Testing.
Advanced Lead Scoring
The process of ranking leads based on their profile data (Explicit Data) and online interactions (Implicit Data). Modern scoring uses Behavioral-Based Automation and machine learning to give a precise, dynamic picture of where a lead is in the Sales Pipeline and their readiness to convert.
Advanced Segmentation
Automatically dividing your audience or contact lists into distinct groups based on multiple, specific attributes (e.g., Visited Page X AND Has a Lead Score over 50 AND Job Title = Director). This enables hyper-personalized messaging and is critical for effective Dynamic Content.
Analytics
The process of collecting, processing, and interpreting data from various digital channels (website, emails, ads, social media) to gain actionable Insights into customer behavior, the Customer Journey, and campaign performance.
Attribution Modeling
The framework used to determine which touchpoints (ads, emails, content) receive credit for a resulting Conversion. Models can range from simple (“First Click” or “Last Click”) to complex multi-touch models (e.g., W-Shaped, Linear).
B
Behavioral-Based Automation
The mechanism of tracking a lead’s real-time online actions (e.g., clicking an email, visiting a product page, submitting a form) and using that information to Trigger an immediate, relevant, and automated marketing action (e.g., sending a follow-up email, changing their Lead Score, or moving them to a different Dynamic List).
Blog
A segment of a website dedicated to timely, engaging, and conversational content. Beyond providing value, blogs are crucial for Content Marketing and driving Organic Traffic via SEO. Short for “web-log.”
Branching Workflow
A fundamental concept in automation where a lead’s path through a sequence is determined by pre-set conditions, typically “Yes/No” or “If/Then” logic. If a condition is met (“Yes”), the lead takes Action 1; if not (“No”), they take Action 2.
Buyer Persona
A semi-fictional, generalized representation of your ideal customer, based on market research and real customer data. Detailed personas define demographics, motivations, pain points, and goals, which inform Segmentation and content strategy. Also known as: Customer Persona.
C
Call to Action (CTA)
An instruction to the audience designed to provoke an immediate response, clearly guiding visitors, leads, or customers on the next desired step (e.g., “Download Now,” “Start Your Free Trial,” “Request a Demo”).
Click-Through Rate (CTR)
A percentage metric measuring the effectiveness of an advertisement, email, or link. Calculated as: $CTR = (\text{Clicks} / \text{Impressions}) \times 100$. Also known as: Click Rate.
Contact
Any individual or entity who has interacted with your business via any channel (form, phone, email, social media). All leads are contacts, but not all contacts are leads. Also known as: Prospect.
Content Management System (CMS)
The application or platform (e.g., WordPress, Drupal, HubSpot) used to create, edit, manage, and publish online content (web pages, blog posts) without needing to write code.
Content Marketing
A strategic approach focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent material (e.g., guides, videos, articles) to attract and retain a clearly defined audience, ultimately driving profitable customer action.
Conversion
The moment a user completes a desired action defined by the marketer, moving them further down the funnel. Examples include filling a form (Lead Conversion) or making a purchase (Sale Conversion).
Cookieless Future
The impending shift, primarily driven by browser policy changes (e.g., Google Chrome sunsetting third-party cookies), that will fundamentally change how marketers track user behavior across different websites. This requires greater reliance on First-Party Data and Data Activation.
Cost Per Lead (CPL)
An advertising metric where the advertiser pays a sum for each individual who shows interest and provides contact information (a lead). Lower CPL is highly desirable.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
A technology system that manages all of a company’s interactions and relationships with customers and potential customers. It collects contact data, establishes Sales Pipelines, and tracks every stage of the Life of the Lead.
D
Data Activation
The process of turning static customer data (collected in a CRM or CDP) into actionable marketing use cases, such as Dynamic Content personalization, Advanced Segmentation, and Behavioral-Based Automation.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail)
An email authentication method designed to prevent email spoofing and phishing. It allows the recipient’s email server to verify that an incoming email was authorized by the owner of the sending domain, thus improving Email Deliverability.
Drag-and-Drop Editor
A type of WYSIWYG editor that allows users with no coding knowledge to build and arrange elements (text blocks, images, forms) in emails or landing pages by selecting and moving them with a cursor.
Drip Campaign
A pre-written, segmented set of marketing messages (typically emails) sent automatically to leads over a defined period of time. This is a foundational technique for Lead Nurturing and onboarding.
Dynamic Content
Content areas (e.g., headline, image, CTA, product recommendation) within a single email or landing page that automatically changes based on the individual recipient’s profile, attributes, or past behavior. This is essential for advanced personalization.
Dynamic Lists
Contact lists that automatically populate and update based on a set of pre-defined, live rules. A contact will automatically be added or removed from the list as their profile data or behavior changes. Also known as: Smart List or Segment.
E
Email Deliverability
The crucial metric that measures the success rate of an email arriving in the recipient’s primary inbox, rather than being routed to spam or blocked entirely. Heavily influenced by sender reputation, DKIM, and content quality.
Email Marketing
Targeting consumers via electronic mail to build loyalty, trust, and brand awareness, often considered one of the most cost-effective methods of direct marketing.
Engagement
Any measurable interaction between a lead/contact and your business, including email opens, website visits, social media comments, or form submissions. A high level of engagement is often a key factor in a high Lead Score. Also known as: Lead Interaction.
Entity Optimization
A modern SEO and AI-focused concept where the goal is to establish your brand/business/author as a verifiable, authoritative Entity in the eyes of search engines, connecting all related data (website, social profiles, third-party mentions) to build trust.
Explicit Data
Information that a lead consciously provides to you, typically through forms (e.g., name, job title, company size). Contrasts with Implicit Data.
F
Filter
A condition used within an automation platform to refine a list of leads or to restrict an automated action. Filters ensure that a specific action only applies to a very narrowly defined group of contacts.
Form
A structured data collection tool embedded on a website or landing page used to gather information from visitors. The completion of a form is often a key Trigger for Lead Generation and automation.
G
Generative AI (GenAI)
A category of artificial intelligence that can create new content (text, images, code, video) based on the data it was trained on. In MarTech, it’s used for drafting emails, creating product descriptions, and automating initial content creation.
I
Implicit Data
Information that a lead unconsciously provides through their online behavior (e.g., pages visited, time spent on site, device used, location). Crucial for Behavioral-Based Automation and calculating Lead Score.
Inbound Marketing
A strategy that focuses on attracting potential customers by creating valuable content and experiences tailored to them. It contrasts with disruptive “outbound” marketing and relies heavily on SEO, Content Marketing, and Marketing Automation platforms.
Insights
The valuable, actionable conclusions drawn from the analysis of marketing Metrics and Analytics, used to inform strategy and make better business decisions.
IP Address (Internet Protocol Address)
A unique numerical label assigned to every device connected to a computer network. In MarTech, Reverse IP Lookup is sometimes used to identify the company name or general location associated with an anonymous site visitor.
L
Landing Page
A standalone web page designed specifically to capture visitor information or drive a single, focused Conversion goal, often with minimal navigation to reduce distraction. Visitors “land” on it after clicking a link from an ad, email, or search result.
Lead
A Contact who has shown definite potential to become a customer based on their profile data, behavior, and/or Lead Score.
Lead Generation
The process of identifying and cultivating new Contacts and attracting them into your Sales Funnel.
Lead Nurturing
The process of building relationships with potential buyers, regardless of their current readiness to purchase. This is typically accomplished through consistent, automated, and personalized communication, often using a Drip Campaign. Also known as: Drip Marketing.
Lead Score
A numerical value assigned to a lead, dynamically calculated based on their attributes (Explicit Data) and engagement (Implicit Data). When a lead’s score hits an established threshold, they become a Sales Qualified Lead (SQL). Also known as: Score, Lead Grade.
Life of the Lead
A complete, chronological record of all interactions between a lead and a business, serving as a unified customer history across all channels and touchpoints. Also known as: Activity Log, Lead Interaction Timeline.
M
Marketing Automation Platform (MAP)
Software-as-a-service (SaaS) that centralizes and automates repetitive marketing tasks (emailing, social media posting, lead scoring, segmentation) to drive leads, convert sales, and measure ROI.
MarTech (Marketing Technology)
A collective term for the software tools and platforms used by marketers to improve effectiveness, measure performance, and achieve marketing goals (e.g., MAPs, CRMs, Analytics platforms).
Media Center
A centralized repository for trackable rich media (videos, PDFs, white papers) that can be linked to in emails or automation Workflows. Crucial for tracking how leads engage with high-value content. Also known as: File Manager, Content Files.
Metrics
General statistics and performance measurements used to quantify marketing activities. Metrics are the raw data points that, when analyzed, yield Insights.
Mobile Optimization
The process of calibrating website pages, emails, and landing pages to display and function seamlessly across various handheld devices (smartphones, tablets). Essential for current web traffic standards. Also known as: Responsive Design.
O
Organic Traffic
Website visitors who arrive naturally from unpaid search engine results (like Google or Bing), as opposed to paid advertisements (PPC) or social media.
P
Page Tracking
The measurement of individual page views and activity on a website, which serves as a core source of Implicit Data for Behavioral-Based Automation.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC)
An internet advertising model where the advertiser pays a fee each time their ad is clicked. The most common examples are search engine advertisements (e.g., Google Ads).
Point-and-Click Editor
An alternative to a Drag-and-Drop Editor or coding, where placing a cursor on an element and clicking activates a function or modification panel. A common interface for editing text and basic layout.
Progressive Profiling
A lead generation technique where forms are designed to dynamically ask new, unique questions on subsequent visits. This collects required information over multiple Touchpoints without discouraging the visitor by asking for too much data at once.
R
Render Testing
The critical quality assurance process of checking how an email or web page appears across various email clients (Outlook, Gmail), browsers (Chrome, Safari), and mobile devices before it is sent/published.
Responsive Templates
Pre-built designs for emails or landing pages that inherently utilize Mobile Optimization (responsive design), ensuring the layout and content adapt efficiently to any screen size.
ROI (Return on Investment)
The primary metric for proving the business value of marketing activities. Calculated as: $ROI = (\text{Net Profit} / \text{Cost of Investment}) \times 100$. A key function of a modern MAP is demonstrating ROI.
RSS Email Syndication (Real Simple Syndication)
The automated process of capturing new content from a website’s feed (e.g., a new blog post) and distributing it instantly to email subscribers.
S
Sales Funnel
A visual metaphor describing the theoretical customer journey, starting with a large number of prospects at the top (Awareness) and narrowing down to a small percentage of converted customers at the bottom (Purchase). Also known as: Conversion Funnel.
Sales Pipeline
A visual, step-by-step representation used by sales teams to track prospects and leads through the various stages of the sales process, typically managed within a CRM.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
The strategic application of techniques to increase the quantity and quality of Organic Traffic to a website by ensuring content ranks highly for specific search terms.
Segmentation
The act of separating a large audience or list of contacts into smaller, more manageable, and homogenous groups based on shared attributes or behaviors. The foundation of personalization.
Site Visitor
Any individual who lands on a website. They are typically anonymous until they convert by providing their information in a Form.
Social Media Conversions
Tracking users who start their journey on a social media platform and ultimately complete a desired action or Conversion on the business’s website.
Social Media Monitoring
The tracking of social media conversations, mentions, and keywords to gather intelligence about a brand, product, or individual.
Split Testing
See: A/B Testing.
T
Third-Party Postback
A technical method (often via a Postback URL) used to securely share collected data between two systems (e.g., sending conversion data from your website’s shopping cart back to your Marketing Automation Platform).
Time-Based Automation
Automation rules initiated based on a fixed schedule (e.g., “send an email every Tuesday”) or a delayed delivery after a specific event (e.g., “wait 7 days after signup, then send email”).
Trigger
A specific event or condition that initiates an automated action or sequence (Workflow) within the marketing automation platform (e.g., “Form Submitted,” “Lead Score Reached 100,” “Page Visited”). Also known as: Automation Rule, Workflow Starting Condition.
W
Workflow
A pre-defined sequence of automated steps, conditions, and actions designed to achieve a specific marketing goal, such as nurturing a lead or onboarding a new customer.
WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get)
A type of user interface (UI) for content editing that allows the user to see the content as it will appear when published (e.g., in an email or web page), eliminating the need for manual coding. Drag-and-Drop and Point-and-Click are forms of WYSIWYG.



